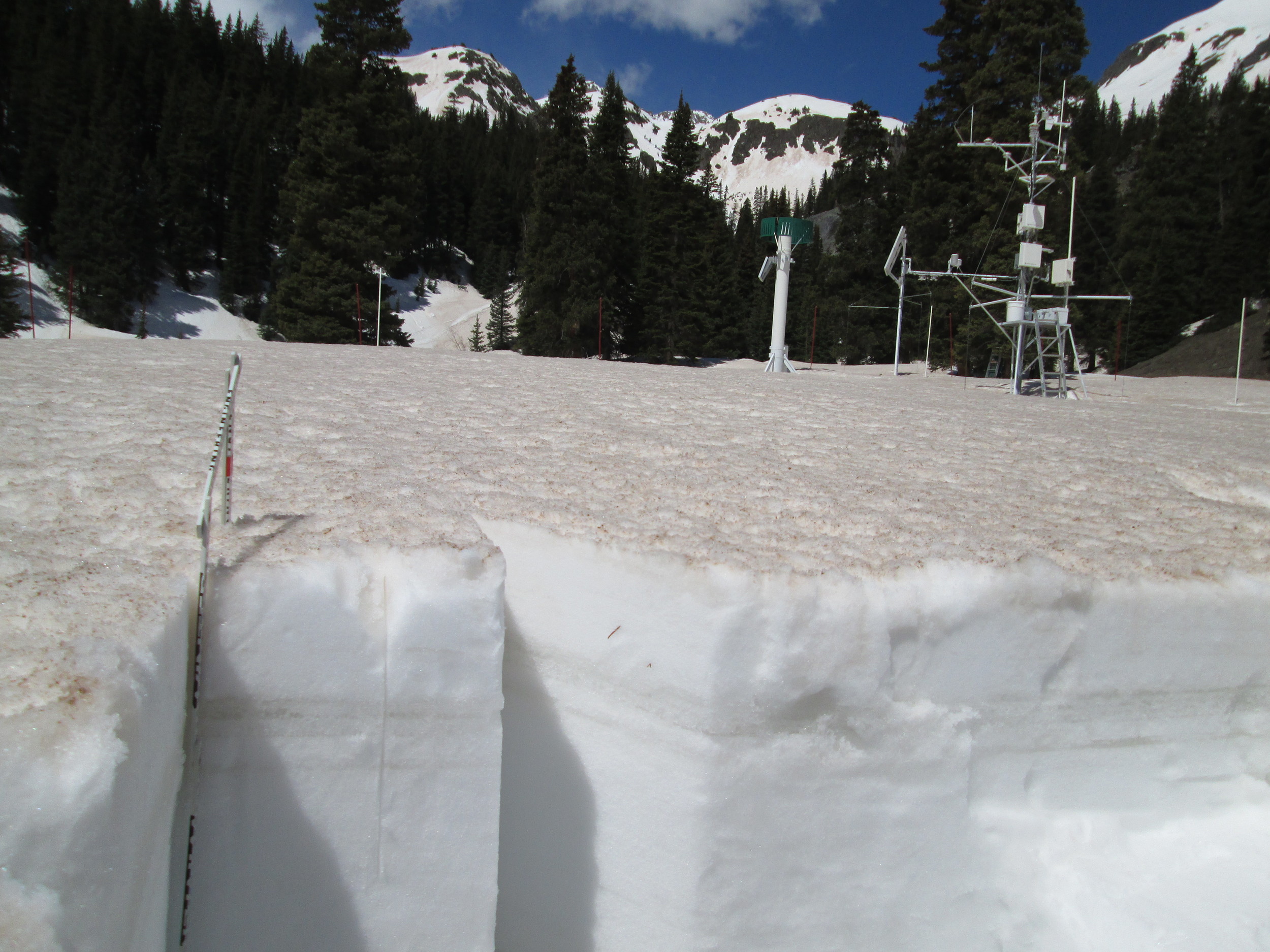
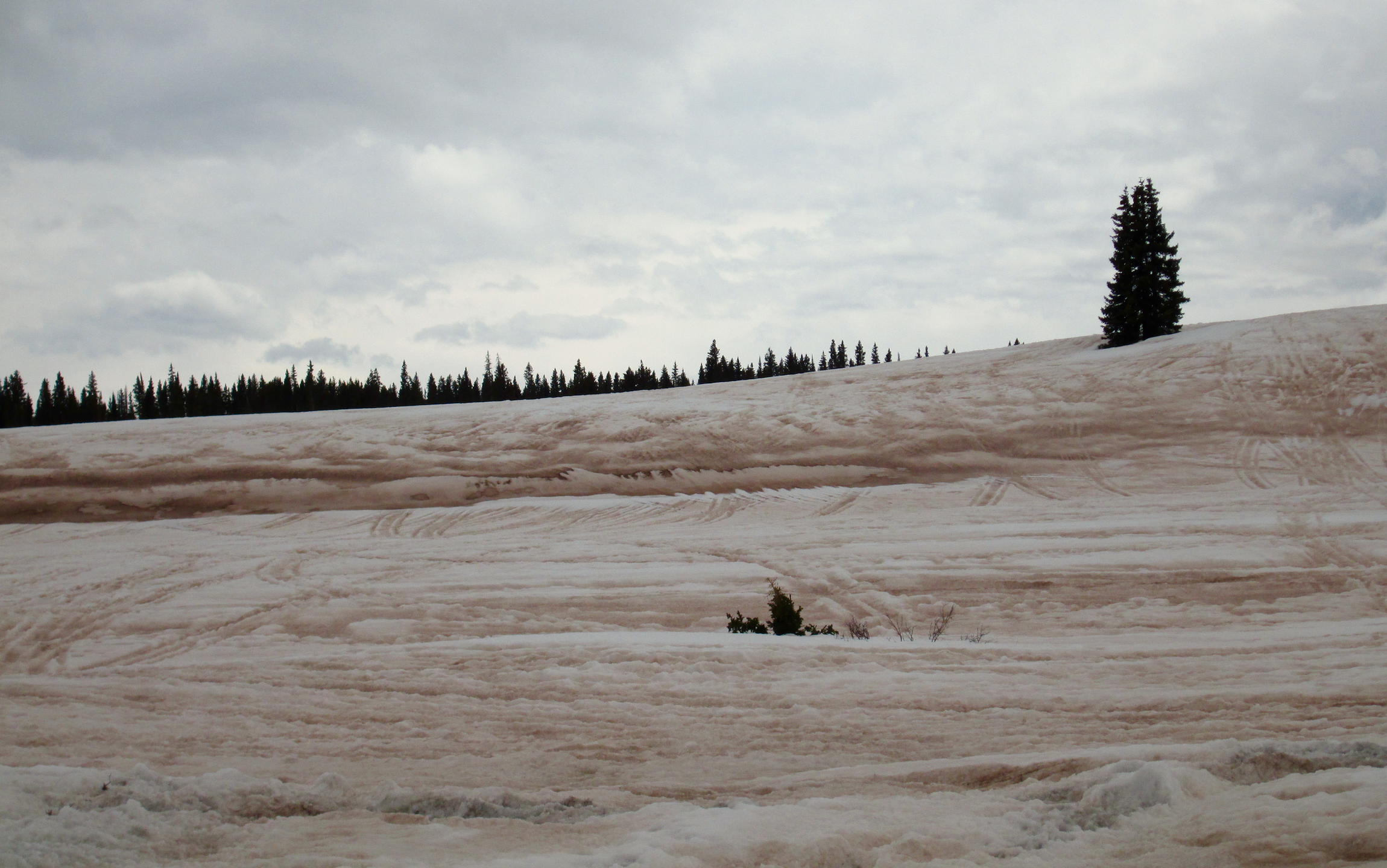
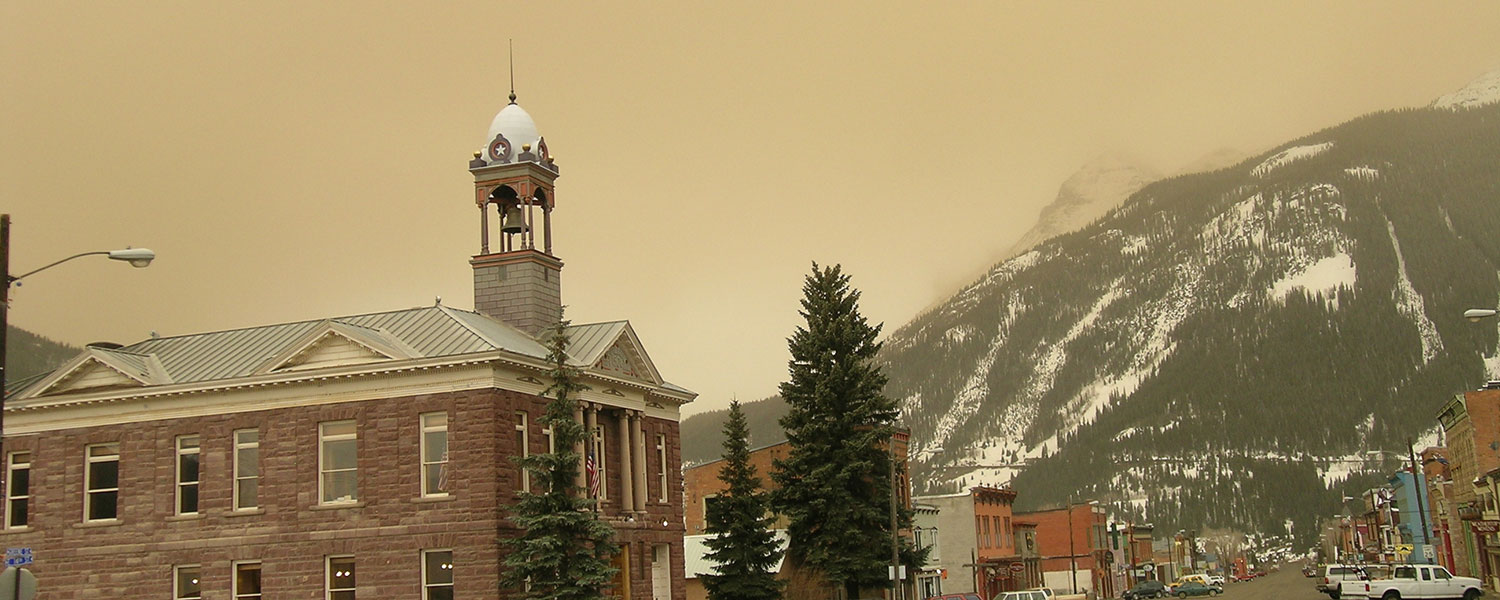
Colorado Dust-on-Snow Program
Colorado Dust-on-Snow Program
The Center for Snow and Avalanche Studies (CSAS) is home to “CODOS”, the Colorado Dust-on-Snow program, an applied science effort on behalf of Colorado and regional water management agencies. CSAS operates the Senator Beck Basin study area at Red Mountain Pass as the primary sentry site for the CODOS program. With direct funding from stakeholders, CSAS monitors the presence/absence of dust layers at 11 mountain pass locations throughout Colorado. Using those observations, data from nearby Snotel sites, and weather forecasts, the CODOS program issues a series of “Update” analyses of how dust-on-snow is likely to influence snowmelt timing and rates during the runoff season.
For a crash course on dust-on-snow read this article published in the Water Report.
5-Minute Video
2-Minute Video
Water Year 2026 Updates
December 18, 2025: Register for Snow School this February 25-27
December 9, 2025: Soil Moisture, San Luis Valley Workshop, Co Gives
November 19, 2025: Winter Begins, Hourly Station Images, Dust-on-Snow Symposium Booklet,….and More
Water Year 2025 Updates
July 21, 2025: WY2025 Season Summary
June 16, 2025: Snow Gone at Senator Beck Study Plot
June 6, 2025: Rain, and a Skimming of Snow
May 29, 2025: Snow Near Gone at Swamp Angel, Still 3’ at Senator Beck
May 15, 2025: Swamp Angel Observations
May 8, 2025: Statewide CODOS Observations
April 29, 2025: Senator Beck Obs, Dust Event Skirted
April 25, 2025: Looking Towards Peak Flow
April 18, 2025: Obs From Senator Beck, Albedo Reset Coming
April 11, 2025: Statewide Dust-on Snow Observations for April, Just a Dusting
March 24, 2025: Dust Event March 18, Swamp Angel Obs
March 17, 2025: Statewide Dust-on-Snow Observations for March
March 2, 2025: Current WY2025 Dust & Snowpack Conditions, Looking Towards Spring
February 17, 2025: Storm Update, Where the Rubber Meets the Road
February 6, 2025: Hot, Dry, and a Little Dust
January 24, 2025: Cosmic Ray Neutron Project
January 20, 2025: Lagging Snowpack for Southern Colorado, Arctic Blast
January 6, 2025: Snowpack Check-In, Still Space in Snow School
December 9, 2024: Major Station Upgrades
December 1, 2024: Microplastics Article, New Radar, New Employee, Colorado Gives, Snow School
November 8, 2024: Nexus of Land and Water Symposium, Winter Kicks Into Gear
November 3, 2024: Snow School For Water Professionals
Download our WY25 snow pit profiles to-date here (combined pdf doc).
Water year 2024 updates
November 3, 2024: WY2024 Season Summary
June 1, 2024: Rising Peaks
May 16, 2024: Nexus of Land and Water - Southwest Initiative on Land Health and Water Resources
May 15, 2024: Statewide Observations May 10-13
May 8, 2024: 100mph Winds = Dust
May 1, 2024: Albedo Reset and a Bit of Precip
April 22, 2024: Statewide Observations
April 10, 2024: More Dust, Senator Beck Obs, Warm-Up Ahead
April 1, 2024: Snowcourse Day, Wee Dust
March 15, 2024: Statewide Dust-in-Snow Observations for March
March 4, 2024: Major Dust Wallop
March 1, 2024: Dust Event #1 of Season
February 15, 2024: We Needed Those Storms, Still Dust Free
January 26, 2024: Waiting for the Next Storm, Predicting Seasonal Dust-on-Snow Severity
January 3, 2024: Slow Start to Snow Season
November 30, 2023: Alpine Plant Community Survey Results, Colorado Gives Day, Snow School
September 20, 2023: “Snow School For Water Professionals”, Season Summary
Water year 2023 updates
September 5, 2023: WY2023 Season Summary
June 8, 2023: Observations from Senator Beck
June 4, 2023: Observations from Swamp Angel
June 2, 2023: Observations from Southern CODOS Sites
May 30, 2023: Snowmelt as we Head into June
May 23, 2023: Still Lot’s of Snow to Melt, Front Range Obs
May 10, 2023: Warm Up, Cool Down, Repeat
April 29, 2023: Time-Out is Over
April 21, 2023: Observations at the Southern CODOS Sites
April 17, 2023: Observations at Front Range Sites
April 6, 2023: Nature of Runoff Season Just Altered Dramatically, Land Health Thoughts
April 3, 2023: Dust Event #4, More Coming
March 24, 2023: Word For WY2023, “Epic”
March 18, 2023: CODOS Tour Observations - Lot’s O’Snow, Min Dust
March 10, 2023: A Tad Bit More Dust, Storms Coming In
March 1, 2023: March 1 Update, Dust Enhanced Runoff Classification, Current Conditions, Looking Towards Spring
February 26, 2023: Big Storm, Mild Dust
February 17, 2023: Snowpack Update
February 1, 2023: Workshop Information & Zoom Link
January 18, 2023: Crazy Storm Cycle, Workshop Reminder
December 5, 2022: Snow School, CO Gives Day, Storm Reports
November 17, 2022: “Snow School For Water Professionals” this February 8-10
WatER YEAR 2022 UPDATEs
August 15, 2022: WY2022 Season Summary
June 30, 2022: Microplastics in Dust-on-Snow Samples Across Colorado Mountains
May 27, 2022: May CODOS Observations
May 14, 2022: Peaks Ahead
May 10, 2022: Another Day, Another Dust Event
May 6, 2022: Buckle-Up
April 30, 2022: Albedo Nosedive, More Wind/Dust in Forecast
April 25, 2022: More Dust (#7) with Precip, Warm Up thru the Week
April 21, 2022: Statewide Obs, Dust Widespread, at/near Surface
April 14, 2022: Dust Like You Read About
April 8, 2022: Swampy Obs, Warm-up then Wind & Precip
April 2, 2022: Brief Update
March 18, 2022: March CODOS Tour-The Good, Bad, and the Ugly
March 6, 2022: More Dust (#3)
March 2, 2022: March 1 Dust Enhanced Runoff Classification, Current Conditions
February 24, 2022: 3” of Precip & Big Dose of Dust
February 9, 2022: Snowpack in Stasis, Wx Shift Coming?
January 21, 2022: Importance of AR’s in Colorado, Workshop Reminder
January 7, 2022: Real-Time SWE from 12,200’, Anyone?
November 19, 2021: Dust/Snow/Flow in the Rio Grande Workshop
WatER YEAR 2021 UPDATES
July 27, 2021: WY2021 Season Summary
June 3, 2021: Snow Near Gone at SASP, High Elevation Melt to Follow
May 27, 2021: Last Couple Weeks of Snowmelt
May 23, 2021: Major Dust Event
May 16, 2021: CODOS Tour Observations May 13 - May 15
May 7, 2021: General Observations II
May 1, 2021: Snowpack Status, Get to Know the Unc and Other Watersheds
April 23, 2021: General Observations
April 16, 2021: Significant Dust Statewide, Another Dust Event April 14
April 10, 2021: Dry, Hot, and Dusty
March 30, 2021: Dust Event #4 Hit Last Night
March 25, 2021: March Dust Tour Part II - Central and Southern Sites
March 22, 2021: March Dust Tour Part I, New Dust Event at Senator Beck
March 11, 2021: Dust Event #2 Observed
March 1, 2021: March 1 Dust Enhanced Runoff Classification, Current Conditions
February 11, 2021: CSAS Survey, Snowpack So Far, Sahara Dust in Europe
January 29, 2021: State of the Snowpack, Minimal Dust
December 22, 2020: State of the Snowpack, WWA’s User Guide, Happy Holidays
November 24, 2020: Winter Outlook, Dust Event #1, WY2021 Research in Senator Beck, Colorado Gives
Data
Dust Enhanced Runoff Classification (new for 2015)
About CODOS

Dust Enhanced Runoff Classification
Dust Enhanced Runoff Classification
DUST-ON-SNOW IMPACTS ON COLORADO HYDROGRAPHS 2006-2021
In our WY 2016 Summary report, and in presentations during Fall 2015, we introduced a refined approach to understanding the impacts of dust-on-snow on Colorado snowmelt runoff ‘patterns’, as reflected in headwater hydrographs. CODOS has observed dust conditions and snowmelt behaviors in Colorado since 2006. It has become apparent, in that period, that the interactions of three primary factors – March 1 SWE, spring dust intensity, and spring weather (precipitation) – comprise a “dust enhanced snowmelt runoff space” (Figure 1). First and foremost among those factors, snowcover water content (i.e., snow water equivalence, or SWE) in Colorado watersheds dictates snowmelt runoff yields and a basin hydrograph’s overall magnitude. March 1 SWE conditions offer a meaningful benchmark in seasonal snowpack formation that also coincides with the onset of ‘dust season’, as 80% of the dust-on-snow events observed by CODOS since 2005 have occurred in March, April and May.
Then, although the presence of dark mineral dust at or near the snowcover surface during daytime always accelerates snowmelt rates by reducing snow albedo and increasing absorption of solar radiation, dust-on-snow does not automatically result in an early runoff cycle. Considerable variation in the overall timing and rates of snowmelt from equivalent snowpacks containing equivalent dust can occur as a result of differences in the number and size of March, April, and May snowfalls. A dry spring, with fewer and smaller spring snowfalls, prolongs dust layer exposure and maximizes dust impacts on snowmelt. A wet spring with frequent, large spring snowfalls results in repeatedly burying exposed dust and restoring high snow albedo, delaying the full impact of dust until a later period of prolonged dust emergence. Hence, besides contributing additional snow to the seasonal total, March, April and May precipitation plays a key role in determining the timing and rate of dust-enhanced snowmelt runoff, from a given snowpack containing dust.
CODOS has now observed twelve seasons of dust-enhanced snowmelt runoff behavior throughout the Colorado mountains (WY 2006-2021). Hydrographs at headwater stream gauges have been evaluated and classified within the framework of this dust enhanced snowmelt runoff space utilizing a 3 x 3 x 3 cell matrix corresponding to general characterizations of SWE, dust intensity, and spring weather, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: a conceptual dust enhanced snowmelt runoff model integrating the interactions of March 1 SWE, dust intensity, and spring precipitation.
In this approach, March 1 SWE classifications are based on NRCS 1981-2010 statistics for Snotel stations proximal to the eleven sites monitored by CODOS. “Average SWE” is defined as a Snotel site’s 1981-2010 median value for March 1, +/- 10%. Values outside that 90-110% of median condition are classified as either High or Low March 1 SWE.
Dust intensity classification is based on dust conditions observed since 2005 at CSAS’s Senator Beck Basin Study Area (SBB). Dust intensity characterization at SBB represents a difficult challenge since dust deposition intensity has, overall, increased during the period of CODOS observations. As such, the notion of “average” dust intensity has changed over that period and may not yet have stabilized. During the past four seasons, in collaboration with USGS, CODOS has collected and analyzed dust mass loading samples and quantified dust loading at SBB. Those measurements have enabled calibration, from snowpit observations and photographs, of prior seasons at SBB using this three-part classification scheme.
Although still a short period of record, during a period of rapidly changing conditions, these characterizations may be sufficient to distinguish one season from another in this tree-part classification scheme. Within this period of record (2006-2021) Water Year 2007 is classified as “Min+” dust intensity and WY 2006 and WY 2010 are considered “Max-“. (Prior WY’s 2004 and 2005 might also be classified as “Min” dust seasons at SBB, relative to subsequent years, but are not included in these analyses due to incomplete observations.) It is further understood that dust intensity at SBB is typically stronger than observed at sites farther downwind, to the north and east. (CODOS resources have not enabled the collection of dust mass loading samples comparable in quality and frequency to those collected at SBB.) Dust intensity characterizations at sites beyond SBB are, in this classification, both tied to “Min”, “Avg”, and “Max” conditions at SBB as well as being site specific and relative to observed “all layers merged” intensity near the end of the season at the given site (i.e., of generally lower ‘absolute’ intensity than SBB).
Spring precipitation classifications are also based on NRCS 1981-2010 statistics for Snotel stations proximal to the eleven sites monitored by CODOS. Average precipitation is defined as a Snotel site’s 1981-2010 median total of March, April, and May measured precipitation, +/- 15%. Values outside that 85-115% of median condition are classified either Wet or Dry. This more generous range in Average precipitation values is utilized in order to capture the larger spatial variation in spring precipitation from convective sources. Given the generally high elevations of these Snotel sites, March, April, and May precipitation is assumed to be snow and no parsing of rain precipitation was attempted. Analyses of annual variances in total March/April/May precipitation since 2006 have been performed and are now posted on all CODOS site webpages.
Using these rules and procedures, the following table classifies WY 2021 conditions at 19 headwater stream gauges associated with the twelve CODOS monitoring sites (including Senator Beck Basin) and associated Snotels that CODOS monitors:
All other Water Years have been similarly classified in the Excel workbook Runoff_Space_by_Region_and_WY.xlsx. Also, similar classifications were performed for each of the headwater stream gauges, by Water Year in Runoff_Space_by_Watershed.xlsx. Finally, links to presentations of these individual stream gauge classification matrices are listed below. They can also be found in the Dust Enhanced Runoff Classification discussion of each CODOS site.

Dust Log & Windroses
Dust Log & Windroses
Wind rose for dust-on-snow event #12 (D12) of WY 2012
Click on each date in the table below for a wind rose image during the dust event (reduced-size example on right). We have estimated beginning and end times of each event based on observations from Silverton, CO. It is reasonable to assume that our skill at detecting dust-on-snow events has improved over time and that we may have failed to observe very small events during the early years of this work. Custom wind roses can be created using our wind rose tool.
D1 |
D2 |
D3 |
D4 |
D5 |
D6 |
D7 |
D8 |
D9 |
D10 |
D11 |
D12 |
|
| WY 2025 | ||||||||||||
| WY 2024 | ||||||||||||
| WY 2023 | ||||||||||||
| WY 2022 | ||||||||||||
| WY 2021 | ||||||||||||
| WY 2020 | ||||||||||||
| WY 2019 | ||||||||||||
| WY 2018 | ||||||||||||
| WY 2017 | ||||||||||||
| WY 2016 | ||||||||||||
| WY 2015 | ||||||||||||
| WY 2014 | ||||||||||||
| WY 2013 | ||||||||||||
WY 2012 |
||||||||||||
| WY 2011 | ||||||||||||
| WY 2010 | ||||||||||||
| WY 2009 | ||||||||||||
| WY 2008 | ||||||||||||
| WY 2007 | ||||||||||||
| WY 2006 | 12/23 |
02/15 |
03/26 |
04/05 |
04/15 |
04/17 |
05/22 |
|||||
| WY 2005 | 03/23 |
04/04 |
04/08 |
05/09 |
||||||||
| WY 2004 | 04/17 |
04/28 |
05/11 |
|||||||||
| WY 2003 | 02/03 |
02/22 |
04/02 |
| Dust-on-Snow Events Documented per Month, by Winter Senator Beck Basin Study Area at Red Mountain Pass – San Juan Mountains |
||||||||||||
| Oct | Nov | Dec | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Total | Wet | Dry | |
| WY 2025 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| WY 2024 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 5 | 0 |
| WY 2023 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 6 | 0 |
| WY 2022 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 11 | 7 | 4 |
| WY 2021 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 7 | 4 | 3 |
| WY 2020 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 0 |
| WY 2019 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 7 | 5 | 2 |
| WY 2018 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 8 | 2 | 6 |
| WY 2017 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| WY 2016 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 6 | 0 |
| WY 2015 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 2 |
| WY 2014 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 10 | 6 | 4 |
| WY 2013 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 0 | 10 | 6 | 4 |
| WY 2012 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 12 | 3 | 9 |
| WY 2011 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 11 | 7 | 4 |
| WY 2010 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 9 | 5 | 4 |
| WY 2009 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 7 | 5 |
| WY 2008 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 7 | 2 | 5 |
| WY 2007 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 8 | 7 | 1 |
| WY 2006 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 8 | 6 | 2 |
| WY 2005 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 1 |
| WY 2004 | 2 | 1 | 3 | na | na | |||||||
| WY 2003 | 2 | 1 | 3 | na | na | |||||||

Updates & Archives
Updates & Archives
WatER YEAR 2020 UPDATES
July 10, 2020: WY2020 Season Summary
May 30, 2020: Snow Gone at SASP, Almost Gone at SBSP, Peak Flows, Low Volumes
May 19, 2020: All Dust Layers Merged, SBSP (12,200’) Melting Fast, Peak Discharge Timeframe, Another Dust Event?
May 12, 2020: Dust Event #1 Emerging Soon, Three Weeks of Rapid Snowmelt
May 5, 2020: May State-Wide CODOS Tour Observations
April 28, 2020: Warm-Up Ahead, Rapid Snowmelt, Swamp Angel Obs
April 19, 2020: CODOS Rabbit Ears and Willow Creek Observations, New Senator Beck Research Publications
April 14, 2020: April CODOS Tour Report
April 7, 2020: New Light Dust Event #2 and #3, Snowpack Obs, COVID-19 Thoughts, This Day in History
March 25, 2020: Second Leg of March CODOS Tour Report
March 19, 2020: First Leg of March CODOS Tour Report
March 11, 2020: Dust Event #1 Showing Itself, Snowpack Conditions, Atmospheric River to the Rescue?
March 2, 2020: March 1 Dust Enhanced Runoff Classification, Snowpack Conditions
February 5, 2020: Weather and Snow Summary, New Assistant, Alamosa Radar Video
January 15, 2020: “Water Report” Article, SBB Station Data Links, Snowpack Observations
December 18, 2019: Weather and Snowpack Summary, Avy Links, Happy Holidays
November 27, 2019 Update: Hello Winter, Snow School, Colorado Gives Day
October 22, 2019 Update: Snow School, SnowEx, IPCC, Etc…
Water Year 2019 Updates
September 21, 2019: WY2019 Season Summary
June 20, 2019 Update: 1” Precip, Wintry Weekend, Journal Publication
June 16, 2019 Update: Melt Rates, Plots, Still Lots of Snow
June 7, 2019 Update: Dust Out, Sun Out, Surf’s Up
June 4, 2019 CODOS Update: CODOS Tour Part II, Dust Emerged at SASP
May 31, 2019 CODOS Update: CODOS Tour Part I, Warm-Up in Forecast
May 28, 2019 CODOS Update: Another Dust Event, SASP Hits Peak SWE Again, Chances of Precip this Week
May 20, 2019 CODOS Update: New Dust Events D5 & D6, 2” New Precip, Stormy Week Continues
May 14, 2019 CODOS Update: D3 Emerging, Dust Event #4, Warm-Up Through Thursday Then More Precip
May 4, 2019 CODOS Update: Dust Present Throughout State, On Top Of Very Big Snowpack
April 29, 2019 CODOS Update: Significant Dust, Precip in Forecast, then Warm Up this Weekend
April 23, 2019 CODOS Update: Data Plots and General Observations
April 16, 2019 CODOS Update: Dust Event Number 3 Observed
April 6, 2019 CODOS Update: Live Graphics Page, DERC and Radiation Plots
March 27, 2019 CODOS Update: March 26 SASP and Red Mt Observations
March 23, 2019 CODOS Update: March 2019 CODOS Tour Summary
March 8, 2019: CODOS Update: D2 Observed, Snow Keeps Coming
March 3, 2019: CODOS Update: March 1 DERC for CODOS Monitoring Sites
February 12, 2019: CODOS Update: Atmo River, Light D1, Snowpack Update
January 23, 2019: CODOS Update: Current Conditions, SNOTEL Plots
December 20, 2018: CODOS Update: Mid-December Conditions
October 25, 2018: CODOS WY2019: Snow School, Nice Start to Water Year 2019
Water Year 2018 Updates
July 27: WY2018 Season Summary
May 24: CODOS Update: Snow Gone at SBSP (12,200')
May 16: CODOS Update: Tour of Front Range & Northern Sites, SASP Observations
May 12: CODOS Update: Dust Alert D8
May 10: CODOS Update: May CODOS Tour Central/Southern Locations
May 8: CODOS Update: D2-D7 Back on the Surface, It's Dirty
May 2: CODOS Update: Dust Fully Emerged at Senator Beck, Currently Getting Buried
April 25: CODOS Update: Dust Emerging at SASP, Elsewhere
April 20: CODOS Update: Dust at Willow/Berthoud/Loveland/Hoosier, New Dust Event D6 and D7
April 18: CODOS Update: April Statewide CODOS Tour Observations WY2018
April 13: CODOS Update: Dust Alert, Major D5 Event
April 6: CODOS Update: Dust Alert D4, Isothermal Snowpack at SASP, Shot of Precip, USGS Plots
April 3: CODOS Update: Statewide April 1 Snow Course Plots and Trends, Brief Dust Update
March 30: CODOS Update: Dust Alert D3, Melt Season, Atmo River Event Coming?
March 23: CODOS Update: SWE Plots, WY2002 Streamflow, Dust Conditions
March 18: CODOS Update: March 2018 CODOS Tour Summary
March 9: CODOS Update: Streamflow, Low Snowpack, General Thoughts
March 2: CODOS Update: March 1 SWE and Dust Conditions
February 21: CODOS Dust Alert D2 - Heavy, Widespread Event
February 5, 2018: CODOS Update: Jan Recap, Delayed D1, Snow School
January 2, 2018: CODOS Update: December Recap, Snow School for Water Professionals
October 24: CODOS WY2018: Snow School, DIA Exhibit, etc.
WATER YEAR 2017 UPDATES & ALERTS
July 13: WY2017 SEASON SUMMARY
June 17: CODOS UPDATE: IMAGES OF DUST STORM, SNOW GONE AT SBSP
June 12: CODOS UPDATE: SBB CONDITIONS UPDATE
June 1: CODOS UPDATE: SNOWMELT CONTINUES, WARMING EXPECTED INTO NEXT WEEK
May 26: CODOS UPDATE MAY 26: D1-D4 RESURFACED AT SENATOR BECK, ELSEWHERE
May 21: CODOS UPDATE: DUST COVERED BY 1' OF SNOW, 1.7" ADDITIONAL SWE AT SBB
May 17: CODOS UPDATE
May 9: WY2017 CODOS TOUR UPDATE
May 1: CODOS UPDATE
April 24: CODOS UPDATE: DUST CONDITIONS, SNOWMELT RATES, AND UNSETTLED WEATHER IN FORECAST
April 14: CODOS UPDATE: APRIL HAZE, CHANCE OF PRECIP IN FORECAST
April 12: APRIL 7-9 WY2017 CODOS TOUR UPDATE
April 10: CODOS ALERT: EVENT D4 WY2017
March 31: CODOS UPDATE-EVENT D3 WY2017
March 24: CODOS UPDATE: EVENT D2, SNOWPACK AT SWAMP ANGEL ISOTHERMAL
March 17: CODOS UPDATE
March 11: CODOS DUST ALERT - EVENT D1 WY2017
March 8: SENATOR BECK BASIN-WIDE SWE ESTIMATIONS FOR FEBRUARY
March 1: CODOS UPDATE - SWE CONDITIONS
January 5: DUST FREE SO FAR AND HEALTHY SNOWPACK
November 1: CENTER FOR SNOW UPDATE
WATER YEAR 2016 UPDATES & ALERTS
August 15: WY2016 SEASON SUMMARY
May 31: D2-D6 MERGED AT SASP
May 6: CODOS GENERAL UPDATE
April 29: D6 VERY FAINT
April 27: APRIL CODOS TOUR UPDATE FOR BERTHOUD AND LOVELAND PASS
April 26: D5 DOCUMENTED AT SENATOR BECK BASIN, AND D6 POSSIBLY COMING VERY SOON
April 21: APRIL WY 2016 CODOS TOUR UPDATE
March 29: DUST EVENT D4
March 27: CODOS UPDATE
March 24: CODOS DUST ALERT: D3
March 8: HAZE ALERT
March 1: CODOS UPDATE- MARCH 1 SWE CONDITIONS
February 19: D2 FOR WY2016 AT SENATOR BECK BASIN
January 25: CODOS UPDATE
December 20: CODOS DUST ALERT - EVENT D1 OF WY 2016
WATER YEAR 2015 UPDATES & ALERTS
July 7: WY 2015 SEASON SUMMARY: COLORADO'S WEIRD WINTER OF 2014/2015 - COLORADO'S DUST-ON-SNOW PROGRAM
June 22: UPDATE-BOUNTIFUL SPRING RUNOFF
June 4: JUNE 4, 2015 UPDATE - RECORD MAY, SURGING JUNE SNOWMELT
April 30: DUST EMERGING IN SAN JUAN MOUNTAINS
April 24: APRIL 24, 2015 UPDATE – CENTRAL & NORTHERN MOUNTAINS, FRONT RANGE
April 15: CODOS DUST ALERT-EVENT D3 OF WY 2015
April 14: CODOS DUST ALERT – POTENTIAL HIGH FOR EVENT D3 OF WY 2015
April 9: CODOS DUST ALERT-EVENT D2 OF WY 2015
April 6: WY 2015 UNFOLDING
March 1: CODOS UPDATE: MARCH 1 SWE CONDITIONS
February 26: NO-DUST ALERT: ARIZONA WEATHER SQUELCHING DUST EMISSIONS
February 16: DRY SPELL, EARLY SNOWPACK WARMING
January 22: NO DUST-ON-SNOW SO FAR, LOOKING AHEAD USING CODOS EXPERIENCE
WATER YEAR 2014 UPDATES & ALERTS
July 25: CODOS WY 2014 Summary
June 15: CODOS Dust Alert - Event D9-WY2014
June 10: CODOS Update - Dust forcing high snowmelt rates statewide
May 29: CODOS Alert for imminent, dust-enhanced surging in snowmelt runoff
May 26: CODOS Update - Upper Gunnison River and North Fork of the Gunnison
May 22: CODOS Update – Senator Beck Basin and Western San Juan Mountains
May 12: CODOS Dust Alert - D8
April 28: CODOS Update - Tour Summary April 23-26
April 28: CODOS Alert for events D6 and D7
April 23: Dust event averted
April 18: Dust event D6-WY2014 is increasingly likely next Tues/Weds
April 16: CODOS Update - Streamflow Surging and Decline, D4 (Re)Emergence
April 4: Senator Beck Basin CODOS Update
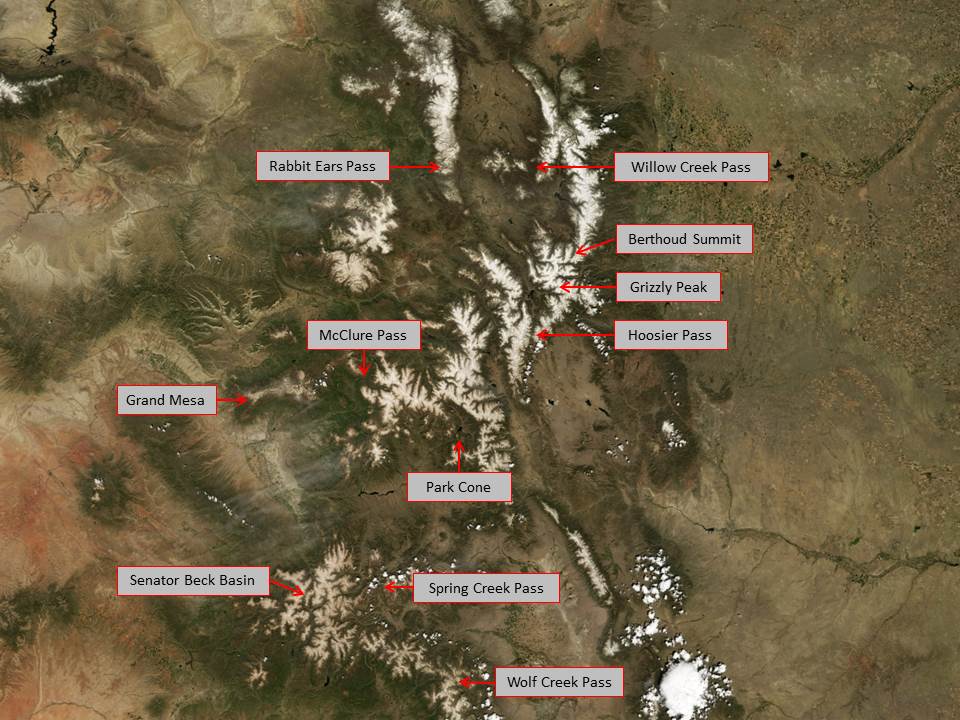
April 1-3 Site Updates: Park Cone | Spring Creek Pass | Wolf Creek Pass | Hoosier Pass | Loveland Pass | Berthoud Pass | Willow Creek Pass | Rabbit Ears Pass | McClure Pass | Grand Mesa
April 1: Dust Alert for D5-WY2014
March 31: CODOS Dust Alert for event D4-WY2014
March 27: CODOS Dust Alert for event D3-WY2014
March 26: Dust storm predicted in NE Arizona
March 18: CODOS Dust Alert for event D2-WY2014
March 17: CODOS Update on Large Snowpacks, Lack of Dust, Runoff Patterns
Feb 6: Windy January without dust
Jan 2: Clean snowcover so far, interesting early winter hydrology
SITE-SPECIFIC REFERENCE & ARCHIVE PAGES
Berthoud | Grand Mesa | Loveland Pass | Hoosier | McClure | Senator Beck Basin | Park Cone | Spring Creek | Willow Creek | Wolf Creek
WATER YEAR 2013 UPDATES & ALERTS
June 17, 2013: Colorado Dust-on-Snow Program WY 2013 Final Report
May 24, 2013: CODOS Update - D10, North to South Variation in Snowmelt
May 12, 2013: CODOS Update for Northern, Front Range, and Grand Mesa CODOS sites
May 7, 2013: CODOS Update for early May conditions at Senator Beck Basin
May 6, 2013: Dust-induced snow surface roughness: time lapse photography and more
April 30-May 1 CODOS Tour of southern sites:
April 30: Swamp Angel Study Plot
: McClure Pass
: Park Cone
May 1 : Spring Creek Pass
: Wolf Creek Pass
April 30, 2013: CODOS Dust Alert - D9, a very minor event at Senator Beck Basin
April 26, 2013: Dust-induced Snow Surface Roughness
April 24, 2013: CODOS Update - D6 and D8 Dust Near Top of Snowpacks Statewide
April 18, 2013: CODOS Dust Alert - D8 event finally over
April 16, 2013: CODOS Dust Alert - D8 now in 36th hour and ongoing
April 14, 2013: CODOS Dust-on-Snow Event Alert - D7-WY 2013, April 13-14
April 10-13 CODOS Tour: Summary
April 10: Swamp Angel Study Plot
April 11: Grand Mesa Study Plot
: Park Cone
April 12: Rabbit Ears Pass
: Willow Creek Pass
: Berthoud Summit
: Spring Creek Pass
: Wolf Creek Pass
April 13: Hoosier Pass
: Grizzly Peak
: McClure Pass
April 9, 2013: D6 A Major Deposition, Many Reports
April 8, 2013: CODOS Alert - Dust-on-Snow Event D6-WY2013
March 25, 2013: CODOS Tour Summary
March 22-23, 2013: CODOS Tour (part 2):
March 22: Swamp Angel Study Plot
March 22: Grand Mesa Study Plot
March 23: Spring Creek Pass
March 23: Wolf Creek Pass
March 22, 2013: Alert for event D5-2013
March 18-21, 2013 CODOS Tour (part 1):
March 19: Berthoud Summit
March 19: Grizzly Peak
March 18: Hoosier Pass
March 20: McClure Pass
March 18: Park Cone
March 20: Rabbit Ears Pass
March 19: Willow Creek Pass
March 21, 2013: Alert for event D4-WY2013
March 8, 2013: D3 Alert and new research on dust enhancement of precipitation
March 1, 2013: Conditions at Senator Beck Basin
February 19, 2013: Update - D2 had limited extent, approaching winter storm to blanket Colorado Plateau
February 9, 2013: D2 Alert
January 25, 2013: Update
January 1, 2013: CODOS Update for New Years 2013
November 30, 2012: Dry start to Water Year 2013
November 9, 2012: 1st dust event of the season (D1)
November 4, 2012: Dry October; Weather and climate websites
Sept 14, 2012: Another important new dust science article just out
September 5, 2012: Recent dust science articles
WATER YEAR 2012 UPDATES & ALERTS
2012 Final Report: A Case Study in Interannual Variability of Colorado Snowpack and the Role of Desert Dust
Berthoud Summit: WY 2012 Summary | May 2 | April 10 | March 28 | March 15
Grand Mesa: WY 2012 Summary | May 1 | April 5 | March 28 | March 16
Grizzly Peak: WY 2012 Summary | April 27 | April 10 | March 28 | March 15
Hoosier Pass: WY 2012 Summary | May 2 | April 9 | March 28 | March 14
McClure Pass: WY 2012 Summary | April 27 | April 11 | March 28 | March 16
Park Cone: WY 2012 Summary | April 27 | April 9 | March 28 | March 14
Rabbit Ears Pass: WY 2012 Summary | May 2 | April 10 | March 28 | March 15
Senator Beck Basin: WY 2012 Summary | April 23 | April 7-8 | March 26-27 | March 5-16
Spring Creek Pass: WY 2012 Summary | April 9 | March 28 | March 17
Willow Creek Pass: WY 2012 Summary | April 27 | April 10 | March 28 | March 15
Wolf Creek Pass: WY 2012 Summary | May 1 | April 9 | March 28 | March 17
Prior Year Updates:
Water Year 2012 CODOS Updates (pdf, 9.5 mb)
Water Year 2011 CODOS Updates (pdf, 5.4mb)
Water Year 2010 CODOS Updates (pdf, 5.4mb)
Water Year 2009 CODOS Updates (pdf, 2.3mb)
Water Year 2008 CODOS Updates (pdf, 0.8mb)

Snotel Datasets
Snotel Datasets
Using the NRCS SNOTEL data, CSAS has assembled datasets presenting Peak SWE and subsequent snowmelt rates at 16 SNOTEL sites distributed throughout Colorado, 11 of which are near a CODOS monitoring site. The remaining 4 SNOTEL sites are in locations between CODOS sites, representing additional terrain. Water Year 2006-2018 Snotel data were examined since this period spans our efforts to monitor dust-on-snow deposition and its effects on Colorado snowmelt behavior. Mean values are calculated for annual datasets representing all fifteen sites, but those averages are intended to be merely descriptive of those years, and not predictive of past or future years. The datasets include:
Peak SWE
Dates of peak SWE
Days to 'Snow All Gone' (SAG)
Daily SWE loss, adjusted for SWE added after peak
Mean temperature (during post-peak SWE period)
Maximum 5-Day Moving Average of Daily Loss of SWE
Number of Dust-on-Snow events after peak SWE
This workbook contains individual spreadsheets for Water Years 2006-2018 and also includes summaries of all 12 years:
WY_SNOTEL_Summaries.xls
Each of these workbooks contain spreadsheets for each year, including a summary aggregating all years for each site:
Beartown | Berthoud Summit | Grizzly Peak | Hoosier Pass | Independence Pass | Lizard Head Pass | McClure Pass | Mesa Lakes | Park Cone | Rabbit Ears Pass | Red Mountain Pass | Schofield Pass | Slumgullion Pass | Upper San Juan | Willow Creek Pass | Wolf Creek Pass

Mass Loading Data
Mass Loading Data

Observations
Observations
We invite you to submit your own dust-on-snow observations. Observations of "no dust" are also welcome. If you have photos, please include a link here or email as attachments to jderry@snowstudies.org

CODOS Site Maps
CODOS Site Maps
For more details, see the CODOS site atlas (pdf) and our Google Earth KMZ file. Contact jderry@snowstudies.org for more information. The first image below is a spring 2009 MODIS satellite image of Colorado's mountain ranges. The cloud tops in the bottom right of the image approximate the color of clean snow.
Senator Beck Basin is outlined in red, with the locations of the four study plots in yellow (from left to right): Senator Beck Study Plot (SBSP), Swamp Angel Study Plot (SASP), Senator Beck Stream Gauge (SBSG), Putney Study Plot (PTSP)

Peer-Reviewed Literature
Peer-Reviewed Literature
Scholarly Dust-on-Snow Related Publications (assisted by CSAS/CODOS):
Doskocil, L.G.; Fassnacht, S.R.; Barnard, D.M.; Pfohl, A.K.D.; Derry, J.E.; Sanford, W.E. Twin-Peaks Streamflow Timing: Can We Use Forest and Alpine Snow Melt-Out Response to Estimate? Water 2025, 17, 2017. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17132017
Reynolds, R. L., Goldstein, H. L., Kokaly, R., Lowers, H., Breit, G. N., Moskowitz, B. M., et al. (2025). Light absorbing particles deposited to snow cover across the Upper Colorado River basin, Colorado, 2013–2016: Interannual variations from multiple natural and anthropogenic sources. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 130, e2024JD041676. https://doi.org/10.1029/2024JD041676
Reynolds, R. L., Molden, N., Kokaly, R. F., Lowers, H., Breit, G. N., Goldstein, H. L., Williams, E. K., Lawrence, C. R., & Derry, J. (2024). Microplastic and Associated Black Particles from Road-tire Wear: Implications for Radiative Effects across the Cryosphere and in the Atmosphere. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 129, e2024JD041116, https://doi.org/10.1029/2024JD041116
Courville ZR, Lieblappen RM, Thurston AK, Barbato RA, Fegyveresi JM, Farnsworth LB, Derry J, Jones RM, Doherty SJ and Rosten SA (2020) Microorganisms Associated With Dust on Alpine Snow. Front. Earth Sci. 8:122.doi: 10.3389/feart.2020.00122
Reynolds, R. L., Goldstein, H. L., Moskowitz, B. M., Kokaly, R. F., Munson, S. M., Solheid, P., et al. (2020). Dust deposited on snow cover in the San Juan Mountains, Colorado, 2011–2016: Compositional variability bearing on snow‐melt effects. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 125, e2019JD032210. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JD032210
Follum ML, Niemann JD, Fassnacht SR. A comparison of snowmelt-derived streamflow from temperature-index and modified-temperature-index snow models. Hydrological Processes. 2019;1–16. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.13545
Arcusa H. S., McKay., N. P., Routson, C. C., Munoz, S. E., (2019). Dust-drought interactions over the last 15,000 years: A network of lake sediment records from the San Juan Mountains, Colorado
Johnson, M. T., Ramage, J., Troy, T. J., & Brodzik, M. J. (2020). Snowmelt Detection with Calibrated, Enhanced‐Resolution Brightness Temperatures (CETB) in Colorado Watersheds. Water Resources Research, 56, e2018WR024542. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018WR024542
Routson, C. C., Arcusa, S. H., McKay,N. P., & Overpeck, J. T. (2019). A 4,500‐year‐long record of southern Rocky Mountain dust deposition. Geophysical Research Letters, 46. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019GL083255
McGrath, D., Webb, R., Shean, D., Bonnell, R., Marshall, H.‐P., Painter, T. H., et al. (2019). Spatially extensive ground‐penetrating radar snow depth observations during NASA's 2017 SnowEx campaign: Comparison with In situ, airborne, and satellite observations. Water Resources Research, 55, https://doi.org/10.1029/2019WR024907.
Arduini, G., Balsamo, G., Dutra, E., Day, J. J., Sandu, I., Boussetta, S., & Haiden, T. (2019). Impact of a multi-layer snow scheme on near-surface weather forecasts. Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems, 11, 4687-4710. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019MS001725
Brown, J. K., Fassnacht R. F., (2019). Snow Depth Measurement via Time Lapse Photography and Automated Image Recognition. Department of Ecosystem Science and Sustainability, Colorado State University. Colorado Water Institute Completion Report No. 233.
Painter, T. H,S. M. Skiles, J. S. Deems, W. T. Brandt, and J. Dozier (2017), Variation in rising limb of Colorado River snowmelt runoff hydrograph controlled by dust radiative forcing in snow, Geophysical Research Letters, 44. https://doi.org/10.1002/2017GL075826.
Zhuojun Zhang, Harland L. Goldstein, Richard L. Reynolds, Yongfeng Hu, Xiaoming Wang, and Mengqiang Zhu (2018), Phosphorus Speciation and Solubility in Aeolian Dust Deposited in the Interior American West, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2018, 52 (5), pp 2658–2667. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.7b04729
ChenglaiWu, Xiaohong Liu, Zhaohui Lin, Stefan R. Rahimi-Esfarjani, and Zheng Lu (2018), Impacts of absorbing aerosol deposition on snowpack and
hydrologic cycle in the Rocky Mountain region based on variable-resolution CESM (VR-CESM) simulations, Atmospheric Chemisrty and Physics, 18, 511–533, 2018. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-18-511-2018
Skiles, S.M. and Painter, T. (2017) ‘Daily evolution in dust and black carbon content, snow grain size, and snow albedo during snowmelt, Rocky Mountains, Colorado’, Journal of Glaciology, 63(237), pp. 118–132. doi: 10.1017/jog.2016.125.
Skiles, S.M., Painter, T. and Okin, G.S. (2017) ‘A method to retrieve the spectral complex refractive index and single scattering optical properties of dust deposited in mountain snow’, Journal of Glaciology, 63(237), pp. 133–147. doi: 10.1017/jog.2016.126.
Guy, Z.M., Deems, J. (2016), Unusual Dry Slab Avalanche Releases Involving Dust-on-Snow Layers in Colorado, Proceedings, International Snow Science Workshop, Breckenridge, Colorado.
Axson, J. L., H. Shen, A. L. Bondy, C. C. Landry, J. Welz, J. M. Creamean, A. P. Ault (2016), Transported Mineral Dust Deposition Case Study at a Hydrologically Sensitive Mountain Site: Size and Composition Shifts in Ambient Aerosol and Snowpack, Aerosol and Air Quality Res., 16: 555-567, doi:10.4209/aaqr.2015.05.0346
Oaida, C. M., Y. Xue, M. G. Flanner, S. M. Skiles, F. De Sales, and T. H. Painter (2015), Improving snow albedo processes in WRF/SSiB regional climate model to assess impact of dust and black carbon in snow on surface energy balance and hydrology over western U.S., J. Geophys. Res. Atmos., 120, 3228–3248, doi:10.1002/2014JD022444
Landry, C. C., K. A. Buck, M. S. Raleigh, and M. P. Clark (2014), Mountain system monitoring at Senator Beck Basin, San Juan Mountains, Colorado: A new integrative data source to develop and evaluate models of snow and hydrologic processes, Water Resour. Res., 50, doi:10.1002/2013WR013711.
Bryant, A. B., T. H. Painter, J. S. Deems, and S. M. Bender (2013), Impact of dust radiative forcing in snow on accuracy of operational runoff prediction in the Upper Colorado River Basin, Geophys. Res. Lett., 40, doi: 10.1002/grl.50773, 2013.
J. Brahney, A.P. Ballantyne, C. Sievers, J.C. Neff. Increasing Ca2+ deposition in the western US: the role of mineral aerosols. Aeolian Research (2013), http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.aeolia.2013.04.003
Deems, J. S., T.H. Painter, J.J. Barsugli, J. Belnap, and B. Udall (2013), Combined impacts of current and future dust deposition and regional warming on Colorado River Basin snow dynamics and hydrology, Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci., 17, 4401-4413, doi:10.5194/hess-17-4401-2013.
Painter, T. H., A. C. Bryant, and S. M. Skiles (2012), Radiative forcing by light absorbing impurities in snow from MODIS surface reflectance data, Geophys. Res. Lett., 39, L17502, doi:10.1029/2012GL052457.
Skiles, S. M., T. H. Painter, J. S. Deems, A. C. Bryant, and C. Landry (2012), Dust radiative forcing in snow of the Upper Colorado River Basin: Part II. Interannual variability in radiative forcing and snowmelt rates, Water Resour. Res., doi:10.1029/2012WR011986.
Painter, T. H., S. M. Skiles, J. S. Deems, A. C. Bryant, and C. Landry (2012), Dust radiative forcing in snow of the Upper Colorado River Basin: Part I. A 6 year record of energy balance, radiation, and dust concentrations, Water Resour. Res., doi:10.1029/2012WR011985.
Painter, T. H., J. Deems, J. Belnap, A. Hamlet, C. C. Landry, and B. Udall (2010), Response of Colorado River runoff to dust radiative forcing in snow, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, published ahead of print September 20, 2010,doi:10.1073/pnas.0913139107.
Lawrence, C. R., T. H. Painter, C. C. Landry, and J. C. Neff (2010), Contemporary geochemical composition and flux of aeolian dust to the San Juan Mountains, Colorado, United States, Journal of Geophysical Research, 115, G03007, doi:10.1029/2009JG001077.
Steltzer, H., C. Landry, T. H. Painter, J. Anderson, and E. Ayres. 2009.Biological consequences of earlier snowmelt from desert dust deposition in alpine landscapes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 106: 11629-11634, doi_10.1073_pnas.0900758106.
Neff, J.C., A.P. Ballantyne, G.L. Farmer, N.M. Mahowald, J.L. Conroy, C.C. Landry, J.T. Overpeck, T.H. Painter, C.R. Lawrence and R.L. Reynolds. 2008. Increasing eolian dust deposition in the western United States linked to human activity, Nature Geoscience, Vol. 1, No. 3, pp. 189-195, March 2008, doi: 10.1038/ngeo136
Painter, T. H., A. P. Barrett, C. C. Landry, J. C. Neff, M. P. Cassidy, C. R. Lawrence, K. P. Thatcher, L. Farmer. (2007) Impact of disturbed desert soils on duration of mountain snow cover. Geophysical Research Letters. V34, 12, L12502, 10.1029/2007GL030208.
Student Theses:
Kevin S. J. Brown, Snow Depth Measurement Via Automated Image Recognition. Watershed Science, Colorado State University (MA 2019)
Caroline Duncan, Forecasting Short-Term Changes in Snowmelt due to Dust Impacts on Snow Albedo, Watershed Science, Colorado State University (MA, TBD).
McKenzie Skiles, Dust and Black Carbon Radiative Forcing Controls on Snowmelt in the Colorado River Basin, Department of Geography, University of California-Los Angeles, (PhD 2014).
Annie Bryant Burgess, Hydrologic implications of Dust on Snow in the Upper Colorado River Basin, Department of Geography, University of Utah, (PhD 2013).
Corey P. Lawrence. Aeolian deposition in the San Juan Mountains of southwestern Colorado, USA: The biogeochemical role of dust in soil development and weathering. Department of Geological Sciences, University of Colorado, Boulder (PhD, May 2009).
S. McKenzie Skiles, MA, Interannual Variability in Radiative Forcing by Desert Dust in Snowcover in the Colorado River Basin, Dept of Geography, University of Utah, projected graduation June 2010.
Kathleen McBride. A synoptic climatology of desert dust deposition to the snowpack in the San Juan Mountains, Colorado, U.S.A., Department of Geography, Northern Arizona University, Flagstaff (MA, December, 2007).
Shane Stradling, An investigation of how dust deposition affects snowpack and snow albedo, Swamp Angel Site, San Juan County, CO, Department of Geosciences, Fort Lewis College, Durango, Colorado (BS, May 2007).

Popular Press
Popular Press
Selected press on CSAS and Dust-on-Snow
Dusty Snow is Making the Western Drought Worse. by Jennifer Oldham. very informative article National Geographic did about dust-on-snow and our CODOS Program, July 14, 2021
Coming Together to Fix a Broken Water Cycle. Durango Herald discussed the consensus workshop in a recent article. December 3, 2021
NASA Hard at Work in Colorado on New Snow Sensing Satellite. by Hannah Stoll, Gazette Telegraph, May 10, 2020
Desert Dust Causes Early Snowmelt and Water Loss, Jonathan Romeo, Durango Herald, May 12, 2018
Dust Speeds Up Snowpack Runoff In Rockies, by Luke Runyon, Here and Now, April 24, 2018
The Rocky Mountains are Dusty, and It's a Problem, by Luke Runyon, NPR, national website, April 22, 2018
The Rocky Mountains are Dusty, and It's a Problem, by Luke Runyon, NPR, KUNC website, April 19, 2018
Colorado Snowpack Struggles in South, Colorado River Basin at 86 Percent, by Brent Gardner-Smith, April 11, 2018
What Dust Can Tell Us About Melting Snow, by Jennifer Meckles, 9 News, April 11, 2018
When Snowpack is the Concern, Science Keeps a Wary Eye out for Dust, by Grace Hood, Colorado Public Radio, April 3, 2018
A Flurry of Research Illuminates Snow's Foes, by Emily Benson, High Country News, March 27, 2018.
Dust-on-Snow Controls Springtime River Rise in West, Carol Rasmussen, NASA, January 24, 2018.
It's Not Just High Temps Messing with Snow - It's Dust, Brad Rassler, Outside Online, February 7, 2018.
What if we could predict water availability with greater accuracy, Mary Shinn, Durango Herald, January 13, 2018
Colorado's Wimpy Winter has skiers, Water Managers Grumbling, Grace Hood, Colorado Public Radio, January 19, 2018.
NASA Seeking to Unlock Secrets of Colorado Snowpack, by Nancy Lofholm. Colorado Public Radio: Colorado Matters, January 5, 2017.
NASA breaking into snow biz, by Dennis Webb. The Daily Sentinel, December 2, 2016.
NASA to study around Silverton as part of satellite development, by Jessica Pace. The Durango Herald, November 26, 2016.
NASA plans a mission to Silverton, by Mark Esper. The Silverton Standard, November 17, 2016.
Lack of red dust from desert means slow and steady Colorado snowmelt, by Jason Blevins. The Denver Post, May 6, 2016.
'Desert Dust' causing Colorado's snowpack to melt early, by Cory Reppenhagen. Denver 7 News Channel, March 27, 2016.
Early Snowmelt on the Rockies threatens Arizona's Water Supply, by Brandon Loomis. Arizona Republic, Aug 20, 2015.
Colorado’s lack of dust, By Dave Buchanan. The Daily Sentinel, April 8, 2015.
Colorado’s Snow is Dust-Free for the First Time in a Decade, by Krista Langlois. High Country News, March 30, 2015.
Dust on Snow Presents Problems in Runoff, by Scott Willoughby. The Denver Post, April 27, 2014.
Dust on Rockies Snow Quickens Melting, Disrupts Water Supplies, by Ana Campoy. Wall Street Journal. Jan 9, 2014
Colorado snowpack off to a poor start, by Bob Berwyn. Summit County Citizens Voice. Nov 7, 2012.
CSAS: Ten Years in Silverton by Chris Landry. The Silverton Standard. October 25, 2012.
Our rapidly shrinking water supply by Eric Ming. The Watch Newspapers, March 2, 2012.
Air Quality Difficult to Gauge in Dustier American West by Kirk Johnson. New York Times, Dec 10, 2011.
Why Development in the Desert Means Lower Rivers and Less Snowpack in the Rockies, By Allen Best. New West Development. November 30, 2011.
Snow Safety: The Inside Scoop with Protect Our Winters, by Penn Newhard. The North Face, Nov. 28, 2011.
Colorado Natural Heritage Program Blog: Cool Climate Collaboration, November 23, 2011
Press in response to the 2010 study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences:
LA Times Blog: Would curbing desert dust help the Colorado River?
Reuters/Yale Environment 360: Dust Hastens Snowmelt in Colorado
NASA News: NASA Funded Study Shows Desert Dust Cuts Colorado River Flow
USGS News: Dust Hastens Colorado River Snowmelt, Cuts Flow: Restoring Desert Soils Could Lessen Impacts of Climate Change
Science and Technology: Desert Dust reduces Colorado River Flow, says new study
NSF: Windborne Dust on High Peaks Dampens Colorado River Runoff
Dust, snow make for problematic mix for skiers by Scott Willoughby. Denver Post. April 20 2010.
Dust on crust: Dusting off wilderness by Will Sanda. Durango Telegraph. April 22 Cover Story.
Dust settling on local peaks has a big impact by Mike Horn. Crested Butte News. April 21, 2010.
Dust in snow causes early melting in region's high country by Scott Rappold. Colorado Springs Gazette.
April 17, 2010.Dust-on-Snow: On Spring Winds, Something Wicked This Way Comes. Earlier snowmelt, altered water supplies, result by Cheryl Dybas. National Science Foundation Discovery. April 2, 2010.
Is Pink Snow Hurting the Vail Valley? - Sarah Mausolf. Vail Daily News. March 24 2010.
Visionaries: Researcher Tom Painter is more worried about dirty snow than global warming - Cameron Walker. Skiing Magazine. Feb/March 2010.
"It started out as a basic question: How is dust affecting the snowpack? Eventually it became a widespread investigation into dust's role in snowmelt, hydrology, and regional climate change, along with how dust might screw up the ski season."
"In 2003, Painter began working on those questions with Chris Landry, ... director of the Center for Snow and Avalanche Studies in Silverton, Colorado."
"When Painter, Landry, and a few colleagues pulled together measurements from Colorado's San Juan Mountains, they found that dust-covered snow melted between 18 and 50 days earlier than dirt-free snow cover."
High stakes snow speculation: gauging our water future - Mike Horn. Crested Butte News. January 27, 2010.
Chris Landry, director for the Center for Snow and Avalanche Studies in Silverton, Colo., traveled around Colorado last spring assessing damage done to the snowpack by the 12 layers of dust (the most ever recorded) that fell starting in October 2008. His findings were alarming.
"What we are observing is snowmelt advanced a month as a result of dust," Landry says. "Instead of water managers dealing with this in 2050 [due to long-term climate change], they're dealing with it now.
Dust levels may have melted snow - Zach Fridell. Steamboat Today. August 21, 2009.
Chris Landry, executive director of the Center for Snow and Avalanche Studies in Silverton, said the unusually high level of dust on the snow could have contributed to the fast melt-off.
Landry said the snow in the study area had 55 grams of particles per square meter in spring 2009, compared to 12 grams per square meter in 2008.
La fonte accélérée des neiges de l'Ouest américain inquiète les agriculteurs: Le phénoméne, provoqué par des tempêtes de poussiére, menace l'irrigation des cultures - Le Monde. June 5, 2009.
Dust storms speed snowmelt in the West - Nicholas Riccardi. Los Angeles Times. May 24, 2009.
Painter [in association with CSAS and the University of Utah Snow Optics Lab] has found that dust can speed up snowmelt by as much as 35 days -- in other words, snow that would normally disappear by May 15 would instead be gone by April 10.
Spring runoff to be fast and furious: Snowpack disapearing because of dust storms; Crystal River nears flood stage - Scott Condon. Aspen Times. May 2009.
Three of the storms that blew in from the Colorado Plateau farther to the west were particularly intense, according to Chris Landry, director of the Center for Snow and Avalanche Studies. Landry, a former resident of the Crystal River Valley, began studying the dust's impacts on the snowpack with Tom Painter of the University of Utah in the winter of 2003-04. They found that a particularly intense dust storm in February 2006 accelerated teh melting of the snowpack by about 30 days that spring. The three dust storms that hit March 22, 29 and April 3 this season equaled the 2006 event in intensity.
Landry said water for crops will be plentiful before farmers need it in large amounts. Less water might be available in July when farmers depend on it.
Landry said that could produce problems for water managers. They will have a shorter time to prepare reservoirs for inflow.
Climate change, water shortages conspire to create 21st century Dust Bowl - Scott Streater. New York Times. May 14, 2009.
Dust storms accelerated by a warming climate have covered the Rocky Mountains with dirt whose heat-trapping properties have caused snowpacks to melt weeks earlier than norms, worrying officials in Colorado about drastic water shortages by late summer.
The Dangers of Dark Snow - Dave Buchanan. The Daily Sentinel [Grand Junction, CO]. May 14, 2009.
Dust on snowpack is a problem. It makes snow darker. And dark snow melts faster. Too fast. In fact, it has a much bigger effect on the snow than global warming.
Dust on the horizon: Record number of dust storms threatens the Southwest - Will Sands. Durango Telegraph. April 30, 2009.
If dust seems mroe severe than before, you're not imagining it. According to Silverton's Center for Snow and Avalanche Studies there have been 13 dust storms so far this winter, the most since the center began tracking them seven years ago.
Dust storms spur environmental fears: Increase in dirt affects ecosystems in Western states - Juliet Eilperin, The Washington Post. April 23, 2009.
...Silverton, Colo., seems an unlikely place for a dust storm, especially with two feet of snow ont he ground. "It was almost surreal," recalled Landry, executive director of the Center for Snow and Avalanche Studies.
"More important, an increasing amount of airborne dust is blanketing the region, affecting how fast the snowpack melts, when local plants bloom and what quality of air residents are breathing."
Rust-red Friday: Massive dust storm blankets much of mountains across centeral, southwest Colorado - Chris Dickey. Gunnison Country Times. April 9, 2009.
"Some longtime weather watchers called Friday's dust storm the worst they'd ever witnessed," according to Chris Landry, who closely monitors "dust on snow" events for the Center for Snow and Avalanche Studies in Silverton.
"Satellite imagery clearly showed that most of the northeastern corner of Arizona was releasing dust plumes heading northeastward..." Landry observed in a report he sends to water watchers...
"Landry reported that Friday actually marked the eighth significant dust event to occur in Colorado this winter season"
"The major ramification is the timing and intensity of snow melt," Landry explained.
Dirt-dusted slopes may hasten mountain snowmelt - Catherine Lutz, Aspen Daily News. March 2009.
" Dust from the Colorado Plateau being deposited on local mountains is not altogether unusual ... but these events are of concern because they may hasten the end of the ski season."
"When exposed at the surface, the dust reduces the reflectivity of the snow, and it directly absorbs solar radiation, so until it's gone the dust is dramatically accelerating snowmelt", said Chris Landry, director of the Center for Snow and Avalanche Studies in Silverton.
"Landry said one study showed snowmelt can be advanced by four to six weeks because of winter dust storms."
Snow Researchers set to do dust hunting: Researchers studying dust effects on snowpack - Idaho Mountain Express. Feb 2009.
" Chris Landry will soon be back out looking for clues to help predict water flows and usage..."
"Landry and his associates now have contracts with eight major water agencies in Colorado..."
"We're quite excited about how this has evolved. It has gone from basic research to fully applied science in a very short time"
Silverton Study Funded in Water Bill - Joe Hanel, The Durango Herald. Feb 13, 2009.
" This year's bill has no large projects in Southwest Colorado, but it does include funding for Silverton's Center for Snow & Avalanche Studies to study effects of dust on snowmelt."
"Recent research from the center has shown that snow covered with a thin layer of dus will melt much earlier than clean snow, possibly causing serious consequences for irrigators.
High Peaks, Dirty Snow - Forest Magazine by Allen Best. Winter 2008
Kicking up dust. How did desert dust land in high-mountain lakes? by Allen Best. Aspen Times, July 2008
National Public Radio devoted stories on CSAS research May, 2006 -http://www.npr.org/templates/story/story.php?storyId=5415308 (Snow effect)http://www.npr.org/templates/story/story.php?storyId=5415315 (Dust emission)
High Country News devoted story ‘Dust and Snow’, May, 2006 http://www.hcn.org/servlets/hcn.Article?article_id=16326 (this story contributed to Michelle Nijhuis’ winning the 2006 AAAS Science Journalism prize)
Backcountry Magazine devoted story ‘Colorado’s dirty little secret’, December, 2006.

Funding & History
Funding & History
Please contact Jeff Derry (jderry@snowstudies.org ) if your agency/organization is interested in joining the CODOS stakeholders.
The Center for Snow and Avalanche Studies is home to “CODOS”, the Colorado Dust-on-Snow program, an applied science effort funded directly by a collaboration of Colorado and regional water management agencies. Research funded in 2004 by National Science Foundation Grant #ATM0431955 showed that winter and spring depositions of desert dust from the Colorado Plateau onto Colorado’s mountain snowpacks can dramatically reduce snowcover albedo, advance snowmelt timing, enhance snowmelt runoff intensity, and decrease snowmelt runoff yields (see Geophysical Research Letter, 2007 and Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2010).
CSAS engaged Colorado’s water management community during the summer of 2006 and has been presenting these findings ever since, at quarterly board meetings of local water districts, Colorado Water Congress and Colorado Water Workshop sessions, regional IBCC Colorado Roundtable sessions, and other technical meetings hosted by the Bureau of Reclamation. With direct funding support from those stakeholders, CODOS monitors the presence/absence of dust layers at ten mountain pass locations throughout the State. With those data, and data from nearby Snotel sites, and given the weather forecasts for those watersheds, CODOS provides its funders and their agency partners with a series of “Update” analyses of how dust-on-snow is likely to influence snowmelt timing and rates during the snowmelt runoff season. That information assists reservoir operators, municipal and agricultural water providers, flood risk managers, and others at local, State, and Federal agencies responsible for managing the spring runoff water that is so vital to Colorado and to states downstream on the Colorado, Rio Grande, North and South Platte, and Arkansas rivers.

CODOS Photo Galleries
CODOS Photo Galleries
Below are links to a selection of CODOS images. Photos for the additional CODOS sites are available on each site page. Displayed is a selection of photos spanning several years of the CODOS program at Senator Beck Basin. All Photos © Center for Snow and Avalanche Studies. Contact Jeff Derry at jderry@snowstudies.org for more information.
Click each photo for a larger version and for captions. Mouse over the large images to display captions, including the date of the photo.
Wind Roses of Dust Events
Wind Roses of Dust Events